What Is Amazon FBA? Discover the Benefits, Costs, and How It Works

Introduction
At Zbao Logistics, we work with thousands of global sellers who rely on Amazon FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) to power their e-commerce success. FBA allows sellers to outsource warehousing, packing, and shipping to Amazon, simplifying the entire fulfillment process.
In this guide, we explain what FBA is, how it operates, the advantages and drawbacks, and how working with an experienced China freight forwarder can help you optimize your FBA logistics.
What Is Amazon FBA?
Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) is a logistics program that lets Amazon handle storage, packaging, shipping, customer service, and returns for sellers. You send your inventory to Amazon’s fulfillment centers, and Amazon takes care of the rest—from receiving orders to delivering them to your customers.
This system allows sellers to focus on marketing, sourcing, and scaling their businesses while Amazon ensures fast, reliable order fulfillment.
How Amazon FBA Works: Step-by-Step
-
Create a Seller Account: Register for an Amazon Seller account and enroll in FBA.
-
Send Inventory to Amazon: Ship goods directly from your suppliers or warehouse to Amazon’s fulfillment centers.
-
Amazon Stores Your Inventory: Amazon scans and stores your items until a sale occurs.
-
Customer Orders: When a customer buys, Amazon picks, packs, and ships the item.
-
Customer Service and Returns: Amazon manages after-sales support and product returns on your behalf.
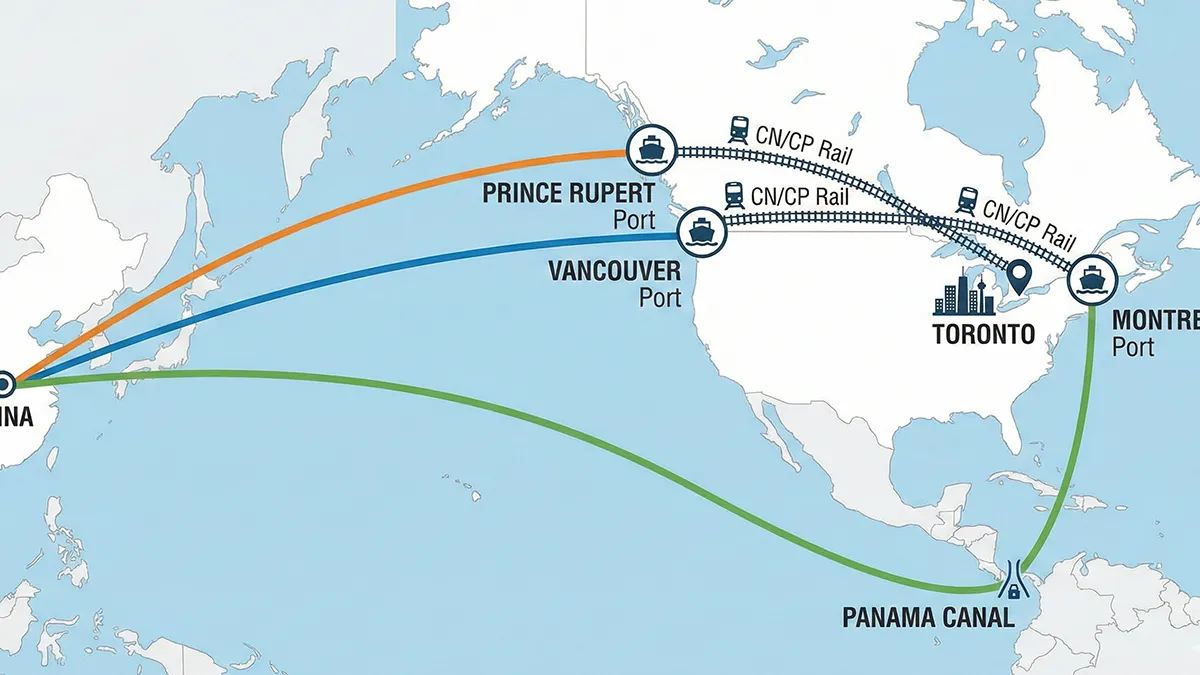
For sellers shipping directly from China, Zbao Logistics provides FBA first-leg shipping services, ensuring your products reach Amazon warehouses safely and on time. Learn more about our FBA shipping solutions.
Key Benefits of Using FBA
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Prime Eligibility | FBA products qualify for Amazon Prime, increasing exposure and conversion rates. |
| Outsourced Logistics | Amazon handles fulfillment, allowing you to focus on marketing and growth. |
| Customer Trust | Buyers trust Amazon’s fast shipping and return policies, improving satisfaction. |
| Scalability | Easily scale operations without expanding warehouse space or hiring staff. |
These advantages make FBA one of the most powerful logistics tools for e-commerce businesses.
Costs of Amazon FBA
While FBA simplifies operations, it comes with specific fees that sellers must manage carefully:
-
Fulfillment Fees: Charged per unit for picking, packing, and shipping.
-
Storage Fees: Based on the space your goods occupy in Amazon’s warehouses.
-
Long-Term Storage Fees: Additional charges for inventory stored over 365 days.
-
Optional Fees: Labeling, removal, and return processing.
Zbao Logistics helps sellers analyze their cost structure and optimize shipments to reduce these fees—especially by consolidating freight from China before it reaches Amazon’s network.
Potential Drawbacks of FBA
Despite its convenience, FBA is not ideal for every seller. Key challenges include:
-
High Costs: FBA fees can impact profit margins on low-priced products.
-
Storage Restrictions: Amazon may impose quantity limits during peak seasons.
-
Complex Rules: Strict labeling and packaging guidelines require precision.
-
Platform Dependency: Heavy reliance on Amazon policies can reduce flexibility.
Our China to USA logistics experts can help you evaluate when FBA makes sense—and when hybrid models like Seller Fulfilled Prime (SFP) or third-party logistics (3PL) may be better.
FBA vs. Other Fulfillment Options
| Model | Description | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| FBA (Fulfillment by Amazon) | Amazon handles warehousing, shipping, and customer service | Prime eligibility, automated operations |
| SFP (Seller Fulfilled Prime) | Seller manages fulfillment but offers Prime benefits | Lower costs, more control |
| 3PL (Third-Party Logistics) | A logistics provider handles fulfillment independently of Amazon | Cost flexibility, brand control |
| Self-Fulfillment | Seller stores and ships all orders directly | Full autonomy, no external fees |
Choosing the right method depends on your volume, budget, and capacity to manage logistics in-house.
Sustainability and Future Growth
At Zbao Logistics, we support sustainable cross-border shipping. We encourage eco-friendly packaging, route optimization, and reduced carbon emissions throughout our China–USA and Europe supply chains.
This aligns with EPA sustainability principles and helps sellers improve their environmental image while reducing waste and costs.
FAQs About Amazon FBA
Q1: How long does it take to send inventory from China to Amazon FBA warehouses?
Typically 15–35 days by sea freight, 7–10 days by air freight, and 2–5 days using express couriers.
Q2: Can Zbao Logistics deliver directly to Amazon warehouses?
Yes, we provide DDP/DDU FBA delivery services with customs clearance and tracking support.
Q3: How can I lower my FBA costs?
Consolidate shipments, optimize packaging, and use a freight forwarder that understands FBA policies and Amazon labeling rules.
Q4: Is FBA suitable for small businesses?
Yes, but profitability depends on product size, margins, and demand. Start small, monitor fees, and scale gradually.
Conclusion
Amazon FBA revolutionized global e-commerce by simplifying fulfillment for sellers.
By partnering with Zbao Logistics, you can connect your China-based suppliers directly with Amazon’s fulfillment network—efficiently, safely, and at lower cost.
We combine freight forwarding, customs brokerage, and last-mile delivery to support your Amazon business from start to finish.
👉 Contact Zbao Logistics today to streamline your next FBA shipment and grow your e-commerce brand globally.