What Does ARO Mean in Shipping? A Complete Guide for Global Sellers
Introduction
In global trade, payment terms shape how smoothly supply chains operate. One of the most common acronyms you’ll encounter in shipping contracts is ARO. But what does ARO mean in shipping?
ARO stands for “After Receipt of Order.” It’s a payment term that directly affects when invoices are due, how businesses manage their cash flow, and the level of trust required between buyers and sellers.
For e-commerce sellers shipping to Amazon FBA, supply chain managers in Europe, and logistics decision-makers in North America, understanding ARO meaning in shipping is critical. This guide will break down how it works, its advantages and risks, and how you can use ARO to strengthen supplier relationships while protecting your cash flow.
What Does ARO Stand For?
The acronym ARO means After Receipt of Order.
In business contracts, ARO specifies that the countdown for payment obligations begins once the seller has received and confirmed an order from the buyer.
👉 Example: If your contract states “Net 30 ARO”, it means the buyer must pay the invoice within 30 days after the seller confirms the purchase order, not after shipping or delivery.
This makes ARO meaning in business particularly useful in industries where production lead times vary, or in international shipping, where delivery dates can shift due to customs clearance or port congestion.
ARO Meaning in Shipping and Business
So, what does ARO mean in shipping?
In logistics, ARO delivery terms set payment expectations before goods even leave the warehouse. The ARO shipping meaning is simple: the payment clock starts once the order is acknowledged.
This differs from other terms like:
-
COD (Cash on Delivery): Payment due upon delivery.
-
ARP (After Receipt of Payment): Seller ships only after payment is made.
By using ARO in shipping contracts, sellers can begin production and fulfillment with assurance of payment within a predictable timeframe, while buyers get a transparent cash flow schedule.
📖 Learn more about international payment terms at the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC)
How ARO Delivery Terms Work
Let’s break it down:
-
Order Placement → Buyer places a purchase order.
-
Acknowledgment → Seller confirms receipt of order (this date starts the clock).
-
Payment Due → Buyer pays within the agreed ARO lead time (e.g., 15, 30, 60, or 90 days).
-
Shipment & Delivery → Goods may arrive earlier or later, but payment is independent of delivery.
👉 Example: If you agree to ARO 30 days, and the seller confirms your order on June 1st, then your payment is due June 30th—regardless of whether the shipment arrives July 5th or July 20th.
This ARO in delivery structure makes it easier to separate financial planning from logistics uncertainties.
Advantages of Using ARO
1. Predictable Cash Flow
Both buyers and sellers can forecast payments with confidence. Buyers know exactly when to allocate funds, and sellers know when cash will arrive.
2. Simpler Operations
Because ARO ties payment to one clear event (order receipt), businesses avoid disputes over when the clock starts.
3. Stronger Relationships
Using ARO delivery terms shows trust and professionalism, which can strengthen long-term supply chain partnerships.
4. Reduced Disputes
Clear deadlines reduce confusion and payment conflicts, which is especially valuable in cross-border trade where multiple parties are involved.
📊 Pro Tip: Many Amazon FBA sellers use ARO contracts with trusted suppliers to free up working capital for marketing and inventory management.
Disadvantages and Risks of ARO
1. Payment Delays
Sellers may face cash flow gaps if buyers delay payments after fulfillment begins.
2. Credit Risk
If the buyer defaults, the seller risks financial loss because production already started.
3. Tracking Complexity
Large companies with multiple orders must track weeks ARO deadlines carefully to avoid missed payments.
4. Limited Flexibility
Changing ARO terms requires renegotiation, which can be complicated in long-term contracts.
📖 See how Investopedia explains payment terms in business finance
How to Use ARO Terms Effectively
For Buyers (E-commerce Sellers & B2B Importers):
-
Use ARO delivery terms to delay cash outflow, giving you time to generate sales before payment is due.
-
Especially useful for Q4 peak seasons like Black Friday, Cyber Monday, and Christmas.
For Sellers (Manufacturers & Suppliers):
-
Offer ARO shipping only to trusted buyers with good credit history.
-
For new customers, combine ARO with partial deposits to reduce risk.
For Supply Chain Managers:
-
Implement ERP or logistics software to monitor ARO payment cycles.
-
Automate reminders to reduce late payments.
📖 Learn more about cash flow management for small businesses at the SBA
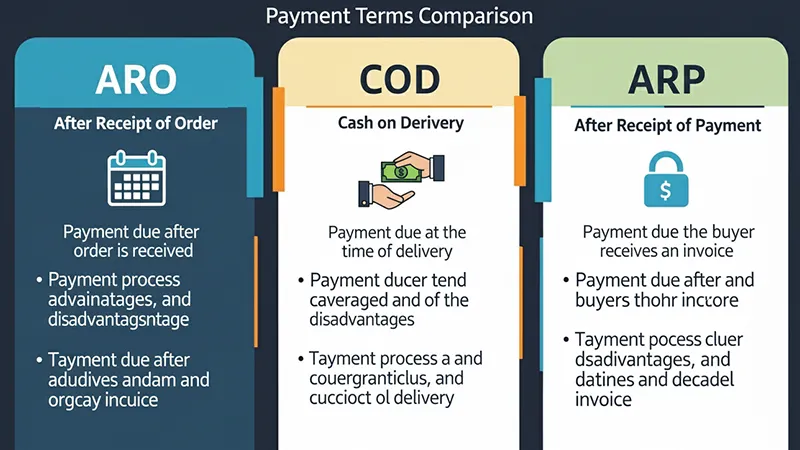
ARO vs. Other Payment Terms
| Term | Meaning | Key Difference |
|---|---|---|
| ARO (After Receipt of Order) | Payment due after order confirmation | Tied to acknowledgment date, not delivery |
| COD (Cash on Delivery) | Buyer pays at delivery | Eliminates delay but requires cash on hand |
| ARP (After Receipt of Payment) | Seller ships only after payment received | More secure for sellers, riskier for buyers |
| Net Terms | Payment due within a set time after invoice | Often used in domestic B2B transactions |
👉 In international shipping, ARO meaning in business strikes a balance: it’s more flexible than ARP, but riskier than COD.
FAQs on ARO Shipping Meaning
Q1: What does ARO mean in purchasing?
In purchasing contracts, ARO means the buyer must pay within a specified time after the order is received and confirmed by the seller.
Q2: Is ARO suitable for international shipping?
Yes. ARO shipping works well for long-term partnerships. However, consider risks like currency fluctuations, banking delays, and customs holds.
Q3: How do businesses track multiple ARO contracts?
Most use ERP systems or logistics management software to track ARO deadlines and automate reminders.
Q4: What happens if buyers don’t pay within ARO lead time?
Sellers may apply penalties, withhold documents (like the Bill of Lading), or delay future shipments.
Q5: What is ARO lead time?
It refers to the number of days (e.g., Net 30 ARO) between order confirmation and the payment deadline.
How Zbao Logistics Helps You Manage ARO
Understanding ARO delivery meaning is just one part of running a smooth supply chain. The other part is having a logistics partner who ensures on-time shipping, customs clearance, and FBA compliance.
At Zbao Logistics, we help:
-
Amazon FBA sellers plan around ARO lead times to maintain cash flow.
-
Importers in North America & Europe ensure goods move seamlessly from China to final delivery.
-
Businesses with multiple suppliers streamline operations with clear visibility into shipments and payment cycles.
👉 Whether you’re navigating ARO in shipping or exploring other payment options, our team ensures your logistics run efficiently and securely.
📩 Contact us today for a free consultation and learn how we can simplify your international shipping.
Conclusion
ARO (After Receipt of Order) is more than just a payment term—it’s a trust-based system that directly impacts cash flow, supplier relationships, and logistics planning.
When managed properly, ARO delivery terms help e-commerce sellers and supply chain managers in North America and Europe operate with more predictability. But success depends on choosing the right partners and having strong tracking systems in place.
By combining knowledge of ARO with the support of an experienced logistics provider like Zbao Logistics, you can transform payment terms from a risk factor into a competitive advantage in your global supply chain.