Understanding CBM in Shipping and Logistics: A Comprehensive Guide
What is CBM (Cubic Meter)?
CBM stands for Cubic Meter, a standard measurement of volume used globally in the logistics and freight industry. It represents the space that cargo occupies within a container, whether for ocean freight, container shipping, or truck transport.
A cubic meter (m³) is simply the volume of a cube with each side measuring one meter. Understanding CBM is essential for both logistics providers and businesses as it directly impacts shipping cost calculations, cargo handling, and container optimization.
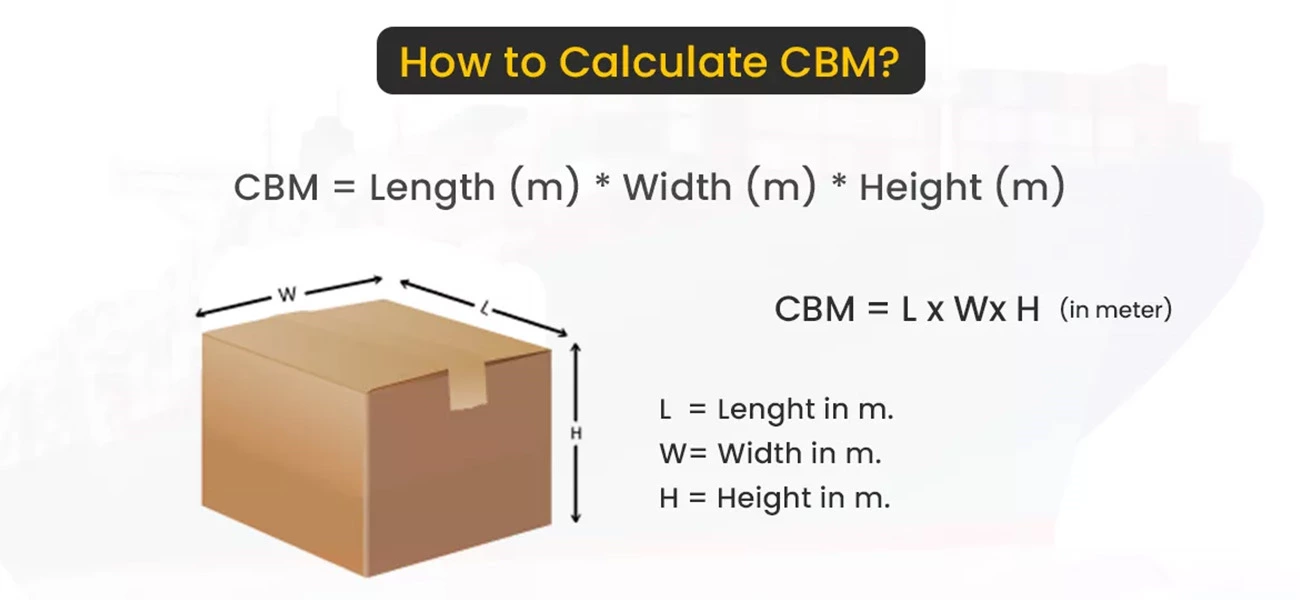
How to Calculate CBM: The Simple Formula
Calculating the CBM of your shipment is relatively straightforward. Here’s the formula:
CBM = Length (m) × Width (m) × Height (m)
-
Measure the length, width, and height of the shipment.
-
Convert all dimensions to meters if they aren’t already.
-
Multiply the three dimensions to calculate the total volume in cubic meters.
For example, if your shipment is 2 meters long, 1 meter wide, and 1.5 meters high, the CBM would be calculated as:
CBM = 2m × 1m × 1.5m = 3m³
This CBM value helps freight companies determine shipping charges and container space requirements.
Why is CBM Important in Shipping?
1. Freight Charges and Costs:
Shipping companies calculate freight charges based on the CBM of your cargo. The more space your goods occupy, the higher your shipping fees will be. CBM is essential for calculating accurate shipping costs per unit volume.
2. Optimizing Container Space:
Understanding the CBM of your cargo ensures efficient container space utilization. Proper calculation helps avoid overloading or under-utilizing shipping containers, ensuring safe and cost-effective transportation.
3. Volumetric Weight Considerations:
In addition to weight, many carriers also charge based on the volumetric weight (calculated via CBM) of your goods. This is especially important for air freight, where volume can sometimes have a greater impact on cost than weight.
Common Mistakes When Calculating CBM
Despite its simplicity, many people make common mistakes when calculating CBM. Here are some errors to avoid:
-
Forgetting Packaging Materials:
Ensure that you account for packaging materials, such as pallets and boxes, when measuring your shipment. These items can significantly affect the total CBM. -
Incorrect Unit Conversions:
Always convert measurements to meters when calculating CBM. For example, 1 inch equals 0.0254 meters, and 1 pound equals 0.453592 kilograms. Using the wrong conversion factor can lead to inaccurate calculations. -
Skipping Double-Checks:
Always double-check your calculations. Even a small error in one dimension can lead to substantial discrepancies in the total CBM, impacting both your costs and the efficiency of your shipment.
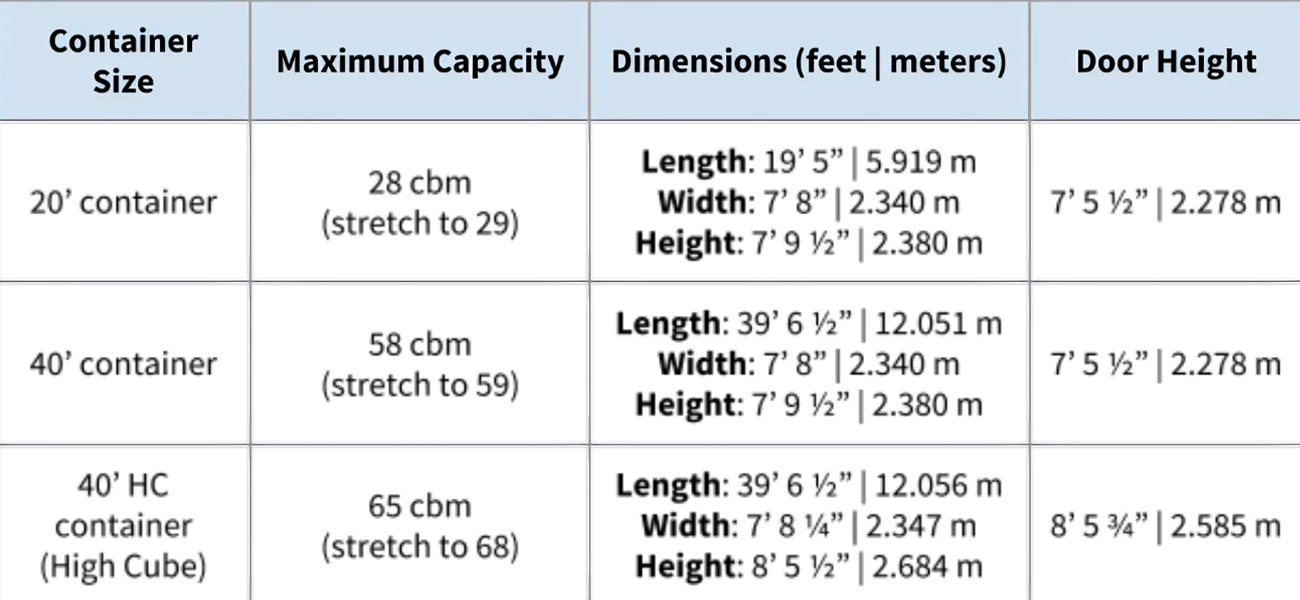
CBM in the Context of International Shipping
In international shipping, knowing your CBM helps prevent overpaying for transportation costs. Freight companies use CBM to determine how much space your shipment will occupy in the container, ensuring that you’re billed correctly. Accurately measuring and calculating CBM allows businesses to optimize their shipping strategies, improving cost efficiency and delivery times.
Final Thoughts on CBM for Shipping
For any business involved in freight, mastering the concept of CBM and how to calculate it is essential. Whether you’re dealing with ocean freight, trucking, or air cargo, understanding CBM helps you make informed decisions regarding your shipments. By knowing how much space your goods occupy in a container, you can better control shipping expenses, optimize logistics, and improve the efficiency of your transportation processes.


