What is a Shipping Carrier? Complete Guide for E-commerce & B2B Sellers
Introduction
Global e-commerce and international trade are growing faster than ever. Products manufactured in Asia are reaching consumers in the U.S. and Europe in record volumes, and B2B supply chains are more connected than at any time in history. Behind all this movement lies one essential question:
👉 What is a shipping carrier, and why does it matter for sellers and procurement managers?
A shipping carrier is the company that physically moves your goods by ocean, air, or land. Carriers are the backbone of logistics, ensuring that containers of electronics, pallets of clothing, or cartons of consumer goods leave factories in China and arrive at fulfillment centers in the U.S., Europe, or elsewhere.
But for e-commerce sellers, Amazon FBA merchants, and B2B procurement teams, the carrier is only one part of the puzzle. Understanding the meaning of carriers, their different types, and how they work with freight forwarders will help you reduce costs, improve reliability, and avoid expensive mistakes.
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know: carrier definitions, examples of carriers, their functions, compliance issues, and most importantly—how to leverage the right logistics partner to grow your business.
What is a Shipping Carrier? (Definition & Meaning)
In logistics, a carrier is defined as:
“An individual or company that undertakes the legal responsibility to transport goods from one location to another by sea, air, or land.”
📌 In other words:
-
A carrier is the transporter.
-
A shipper is the sender of goods (often you, the seller or procurement manager).
Examples of well-known carrier shipping companies include:
-
Maersk (ocean carrier, container shipping giant)
-
FedEx & UPS (integrated air and land carriers)
-
COSCO, Evergreen, Hapag-Lloyd (ocean carriers with global networks)
Carriers are responsible for:
-
Cargo handling (loading, stowing, unloading)
-
Transporting goods safely and on time
-
Complying with international trade laws and safety standards
For official definitions, see the Federal Maritime Commission (FMC), which regulates ocean carriers serving the U.S., or the World Trade Organization for global trade frameworks.
The Function of a Carrier in Global Trade
Carriers serve several critical functions:
-
Transport → Moving goods by vessel, aircraft, or truck.
-
Risk Management → Ensuring cargo safety, offering liability coverage, and complying with regulations.
-
Connectivity → Linking different regions of the world, enabling global commerce.
-
Efficiency → Operating fixed schedules, optimizing routes, and offering scalable capacity.
💡 Example of Carrier Function:
Imagine a seller in Shenzhen exporting 500 cartons of electronics to Germany. The ocean carrier (e.g., COSCO) transports the container by ship. On arrival, a land carrier (trucking company) delivers the cargo from Hamburg port to the Amazon DE fulfillment center. Without carriers, this global chain would not exist.
Major Types of Carriers in Shipping
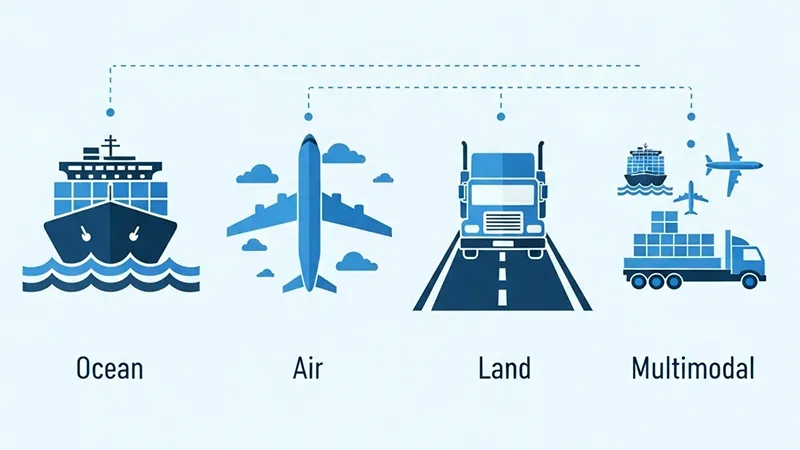
1. Ocean Carriers (Ship Carriers)
Ocean carriers operate container ships, bulk carriers, and roll-on/roll-off vessels. They are essential for large-scale shipments, wholesale orders, and bulk replenishments.
-
Best For: Heavy, bulky, and non-urgent cargo.
-
Advantages: Lowest cost per unit, global coverage, suitable for containers and bulk.
-
Disadvantages: Long transit times, exposure to port congestion, weather risks.
👉 Internal Resource: Amazon Warehouse Locations Guides
2. Air Carriers
Air carriers use cargo planes or passenger aircraft with cargo holds. This method is often used by e-commerce sellers shipping smaller batches to avoid stockouts.
-
Best For: High-value, urgent, or perishable goods.
-
Advantages: Fastest method, high security, reliable schedules.
-
Disadvantages: Expensive, limited volume, environmental concerns.
📌 See the International Air Transport Association (IATA) for global standards on air carriers.
3. Land Carriers
Land carriers include trucking companies, rail operators, and regional delivery services. They are vital for domestic shipping and the final-mile leg of international deliveries.
-
Best For: Short to medium distance shipments, domestic distribution.
-
Advantages: Flexible routes, lower cost for regional deliveries.
-
Disadvantages: Road congestion, cross-border delays, infrastructure limits.
4. Multimodal & Intermodal Carriers
-
Multimodal Transport: One contract covering sea + trucking + rail.
-
Intermodal Transport: Multiple contracts for each mode, but goods stay in the same container.
💡 For Amazon FBA sellers: multimodal transport often combines ocean freight + U.S. trucking for seamless delivery to fulfillment centers.
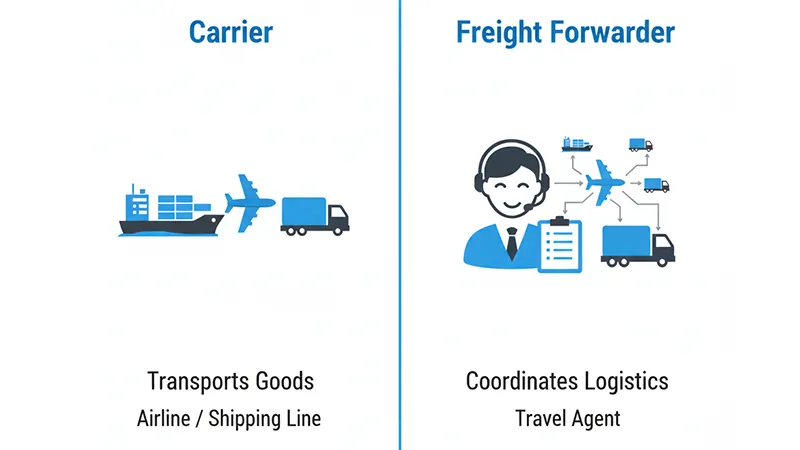
Carrier vs. Freight Forwarder
Many sellers confuse the two. Here’s the difference:
-
Carrier = the company that owns the ship, plane, or truck.
-
Freight Forwarder = your logistics partner that arranges the whole journey.
Think of it this way:
-
Carrier = Airline
-
Freight Forwarder = Travel agent that books your ticket, finds connections, and arranges your hotel and visa.
👉 Internal Resource: China Freight Forwarder Guide
For most e-commerce and B2B sellers, working directly with a carrier is impractical. Carriers demand large shipping volumes and strict schedules. Freight forwarders like Zbao Logistics aggregate multiple sellers’ cargo, secure better rates, handle customs, and ensure on-time delivery.
How to Choose the Right Carrier
When evaluating a carrier shipping company (or freight forwarder’s carrier selection), consider:
-
Type of Goods → Is it lightweight, perishable, or bulk?
-
Destination & Routes → Does the carrier serve your market (U.S., Europe)?
-
Transit Time vs Cost → Fast (air) vs. affordable (ocean).
-
Carrier Contracts → Liability clauses, demurrage, detention.
-
Customer Service → Is there real-time tracking and transparent communication?
👉 Internal Resource: DDP vs FBA Shipping Guide
List of Shipping Companies in the USA
Examples of well-known carriers:
-
Global Ocean Carriers: Maersk, Hapag-Lloyd, Evergreen, COSCO
-
Air Carriers: UPS Airlines, FedEx Express, DHL Aviation
-
Land Carriers: Schneider National, J.B. Hunt, Swift Transportation
-
Regional & Specialized: Ironfox Shipping, Trinity Shipping, TSI Shipping, Northwest Shipping, Dix Shipping, Connect Ship
📌 Note: While these carriers are reputable, negotiating directly is challenging for small and mid-sized sellers. A freight forwarder bridges this gap, providing access to multiple carriers under one service contract.
Challenges & Compliance in Carrier Shipping
Carriers face multiple challenges that can affect your supply chain:
-
Port congestion & weather delays
-
Geopolitical risks (trade wars, sanctions, Red Sea disruptions)
-
Fuel cost volatility & surcharges
-
Security risks (cargo theft, piracy)
Compliance requirements:
-
IMO → Maritime safety & environmental standards
-
FMC → U.S. ocean freight regulations
-
FMCSA → Trucking compliance in the U.S.
For sellers, compliance can feel overwhelming—which is why freight forwarders play a crucial role in managing paperwork, customs, and carrier regulations.
FAQs About Shipping Carriers
Q: What does carrier mean in shipping?
A carrier is a company that physically transports goods by sea, air, or land.
Q: What is the difference between a carrier and a shipper?
-
Carrier = transporter (Maersk, FedEx).
-
Shipper = seller/exporter who sends the goods.
Q: What is an example of a carrier?
Maersk (ocean), FedEx (air/land), UPS (integrated carrier).
Q: What is the function of a carrier?
Transporting goods safely, efficiently, and in compliance with regulations.
Q: Can I work directly with a carrier?
Only if you ship very large volumes. Most small and medium businesses rely on freight forwarders.
Why Work with Zbao Logistics?
Whether you’re an Amazon FBA seller, an independent e-commerce store owner, or a B2B procurement manager, choosing the right carrier determines your logistics success.
At Zbao Logistics, we:
-
Partner with leading carriers worldwide under first-tier contracts
-
Offer flexible shipping solutions (ocean, air, land, multimodal)
-
Handle customs clearance and compliance in both China and destination countries
-
Deliver on-time to Amazon warehouses, retail distributors, or direct customers
👉 Ready to reduce costs and simplify your global shipping?
Contact Zbao Logistics today for a free consultation and customized shipping plan.


